What is a Robot
What does it mean for a robot to be autonomous
Touch Sensor, Sonar
Sensor
Parts of a Robot
What are Effectors
Degrees of Freedom
Gear Ratio
Classes of robot control
Deliberative
Reactive
Sensor Noise
Passive vs. Active sensors
Calibration
What is Locomotion
Compare Static to Dynamic Stability
Differential Drive Motor
Algorithm
Multitasking
Feedback Control
Feedback Control
Input
Controller
Output
Sensors
Actuators
Feedback
Error
Why have Robots work in Teams?
Coordination Strategy of Robots
Light Sensor
Bump Sensor
Wait
Switch (Conditional)
Loop
Write Algorithms/Flowchart (Such as the sample one below).
Variable
Communication Protocol
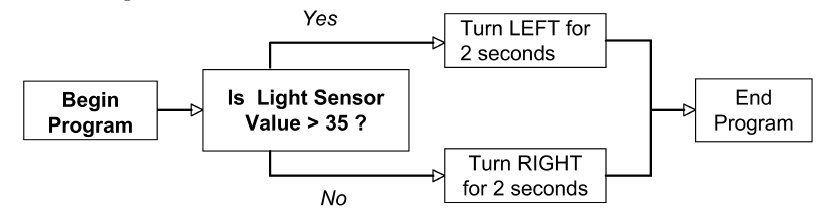
Be able to draw out
a flow charge such as:
If the Light Sensor is above 35, turn left for 2 seconds, otherwise
turn right for 2 seconds.
The following is the solution for the flow chart.

From the above flowchart, if the robot is turning to the right, what is known about the light
sensor reading?
Have a loop checking the sonar sensor. While the sensor reading is under 20, have motors B & C move forward. Otherwise have the motors stop.
Have the robot move forward constantly unless the bump sensor is pressed. If the bump sensor is pressed, have the robot backup for 3 seconds, and turn to the left 45 degrees. Keep having the robot move infinitely.
Have the robot move forward towards a wall. A light bulb will take as an input from a variable to adjust the brightness of the light. Have the robot move forward towards a wall and the light will get brighter. If the distance is under 10 cm, stop the robot. Write up a flowchart to make this work. Use a variable to store the sonar distance in a variable called brightness (but using a formula, as the distance gets closer towards the wall (lower values) the brightness cannot mearly be the distance value. Try it for 100cm from the wall).