Hardware Components of a Computer
- Main Memory, also known as RAM (= Random Access Memory), or simply "memory", is a chip that stores the values of variables, arrays, and objects, as well as all the currently running programs' instructions. Every program is built up of instructions, and every program uses variables (such as the arguments and return value from the main() function), which means every program resorts to storing data in memory during its execution.
Memory is a volatile device: once the computer is turned off, the data in it is deleted.
Closeup of a 2GB Memory Stick. Miriam Briskman, CC BY-NC 4.0.
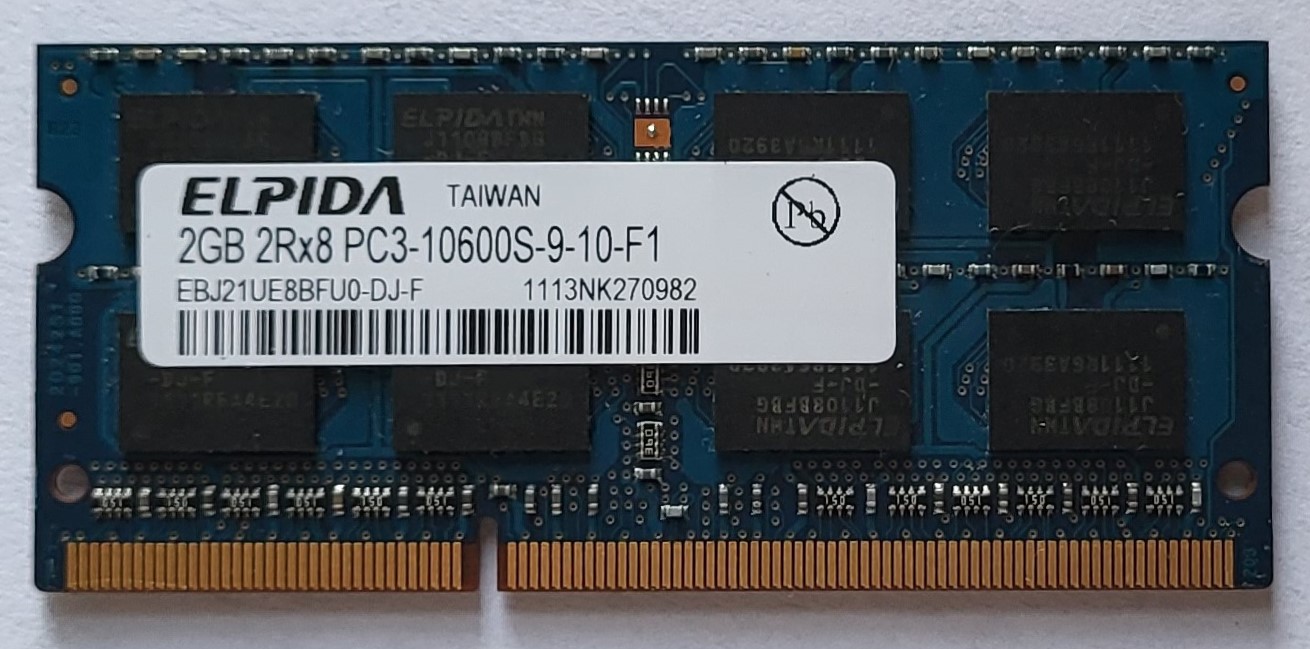

The Blue 2GB Memory Chip, Front. Miriam Briskman, CC BY-NC 4.0.
