Mechanical Aids: Rotor Machines
A Rotor Machine is an electro-mechanical stream cipher device used for encrypting and decrypting secret messages. Such machines were used in the 1920s - 1970s, with the Enigma system being one of its known examples. A rotor machine has rotating disks with an array of electrical contacts on either side. Such a machine implements a fixed substitution of letters, replacing them in a complex fashion.
Specifically, after encrypting each letter, the rotors advance positions, changing the substitution and producing a complex substitution cipher, which changes with every keypress.
During WWII, the Allies broke the encryption of the Enigma machine by analyzing how wires were connected to the machine's rotors and using knowledge about permutations.
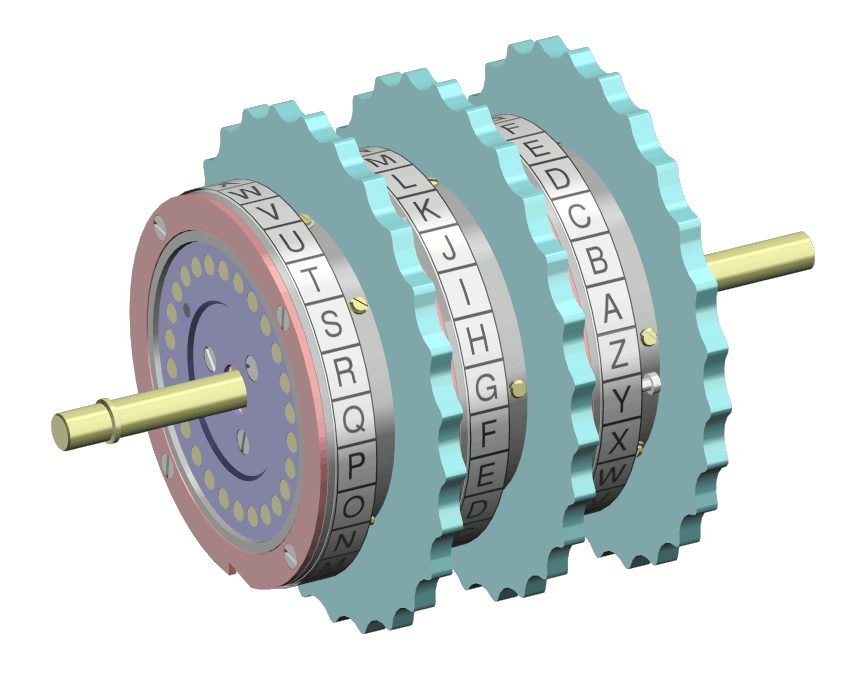
Enigma rotor set. Wapcaplet This image was created with Blender., CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons
